Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects a child’s social interactions, communication skills, and behavior. While every child develops at their own pace, there are specific developmental milestones that, when delayed or absent, can indicate the possibility of autism. Understanding these milestones and recognizing the early signs of autism can help parents seek early intervention, which is critical for supporting the child’s growth and development.
What is Autism and Developmental Milestones?

Developmental milestones are the skills or abilities that most children achieve by a certain age. These milestones span areas such as language, motor skills, social interaction, and cognitive development. Children with autism often experience delays or differences in these areas, particularly in social and communication skills. Recognizing these delays early can lead to timely interventions that support the child’s development.
Typical Developmental Milestones:
- By 6 Months: Smiling, making eye contact, responding to sounds.
- By 12 Months: Babbling, pointing, showing objects to others, recognizing their name.
- By 18 Months: Saying simple words, engaging in pretend play, following simple instructions.
- By 24 Months: Using two-word phrases, showing interest in other children, playing simple games.
While these milestones are typical for most children, children with autism may show delays or differences in achieving them.
Early Signs of Autism in Toddlers
Autism can manifest in various ways, but there are common signs parents can look for in toddlers. These early signs may appear before the age of two and often involve delays in social and communication skills, as well as repetitive behaviors. Here are some of the early signs:
1. Limited Social Interaction
- Lack of eye contact.
- Rarely responding to their name.
- Prefers to play alone rather than with other children.
2. Speech and Language Delays
- Delayed speech development or loss of previously acquired language skills.
- Repetitive speech or echolalia (repeating phrases or sounds).
- Difficulty using gestures like pointing, waving, or nodding.
3. Repetitive Behaviors and Routines
- Engaging in repetitive movements like hand-flapping, rocking, or spinning.
- Insistence on following specific routines and becoming upset with changes.
4. Sensory Sensitivities
- Unusual responses to sensory input, such as hypersensitivity to noise, lights, or textures.
- Seeking sensory stimulation, like spinning objects or watching moving parts for extended periods.
Recognizing these signs early on can help parents seek a developmental evaluation for their child.
The Diagnosis Process for Autism
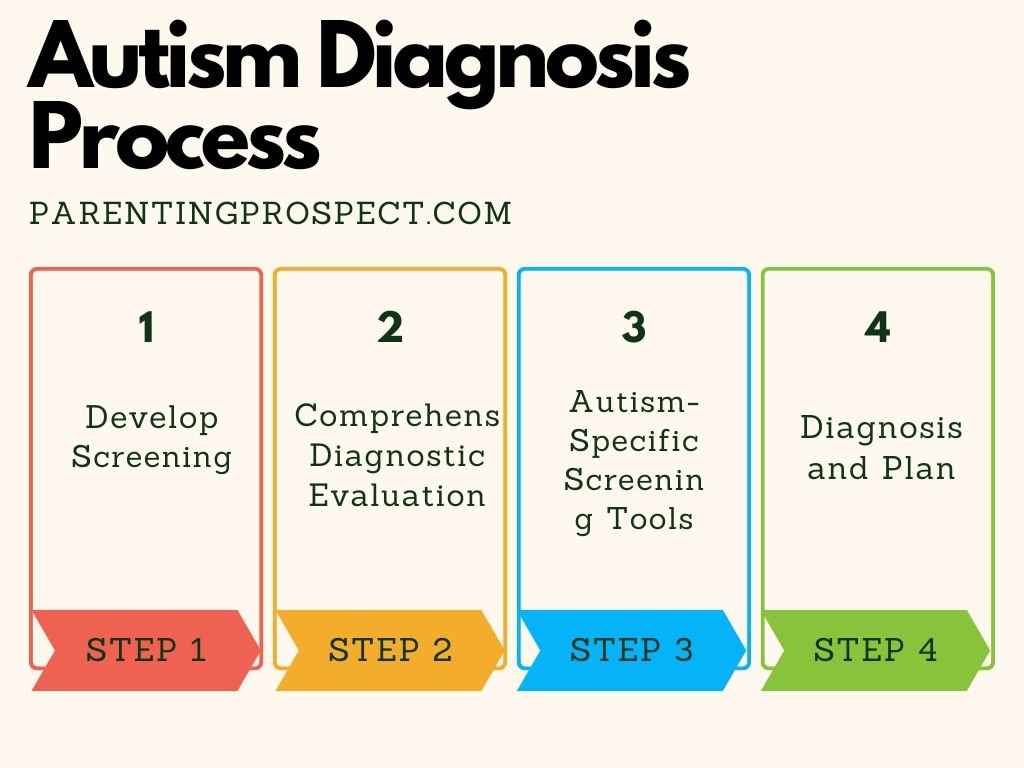
If you notice signs of autism in your child, the first step is to speak with your pediatrician. Early diagnosis is key to providing the right support. The diagnosis process typically involves:
1. Developmental Screening
Developmental screenings are brief tests that assess whether a child is meeting typical developmental milestones. During well-child visits, your pediatrician may conduct these screenings to monitor your child’s progress.
2. Comprehensive Diagnostic Evaluation
If developmental delays or signs of autism are present, your pediatrician may recommend a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation. This involves assessments by specialists such as developmental pediatricians, In-Home Child Care psychologists, and speech-language pathologists. These evaluations assess social, communication, and behavioral patterns to confirm a diagnosis.
3. Autism-Specific Screening Tools
There are specific tools used to assess autism, such as the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) and the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS). These tools help identify behaviors and patterns that are characteristic of ASD.
4. Diagnosis and Plan
Based on the results, the child may be diagnosed with autism, and a personalized intervention plan is created to provide appropriate support and therapies.
Early Intervention and Support
Early intervention is crucial for children with autism. Interventions help support the development of communication, social, and behavioral skills, and can significantly improve a child’s quality of life. Common interventions include:
1. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
ABA therapy focuses on improving specific behaviors, such as communication, social skills, and self-care, through positive reinforcement and structured teaching.
2. Speech Therapy
Speech therapy helps children with autism develop communication skills, whether through verbal language or alternative communication methods such as sign language or picture-based systems.
3. Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy addresses sensory sensitivities, fine motor skills, and daily living activities to help children become more independent.
4. Social Skills Training
Social skills training helps children learn how to interact with others, read social cues, and engage in group activities. These skills are essential for making friends and functioning in social settings.
Final Touch
Recognizing the signs of autism and developmental delays early allows parents to seek the necessary support and interventions to help their child thrive. While autism presents challenges, early diagnosis and therapy can make a significant difference in a child’s life. Remember, every child with autism is unique, and with the right support, they can reach their full potential.
FAQs About Autism and Developmental Milestones
If you suspect your child has autism, speak with your pediatrician immediately. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical for supporting your child’s development.
Autism is diagnosed through developmental screenings, comprehensive evaluations, and autism-specific assessment tools. The process usually involves multiple specialists.
Autism is a lifelong condition, but early intervention and therapies can help children develop skills to manage their challenges and improve their quality of life.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training are commonly used therapies that help children with autism develop essential skills.


